The zero conditional sentences or real conditional describes true things. We describe a real situation using the zero conditional or a very probable situation in the present or future. We can also use zero conditional to talk about rules, habits, universal truth, and instruction. But every sentence declaring a fact is not a conditional sentence. A conditional sentence must have two clauses, the if-clause/conditional clause and the main/result clause.
Zero Conditional Sentences Formula
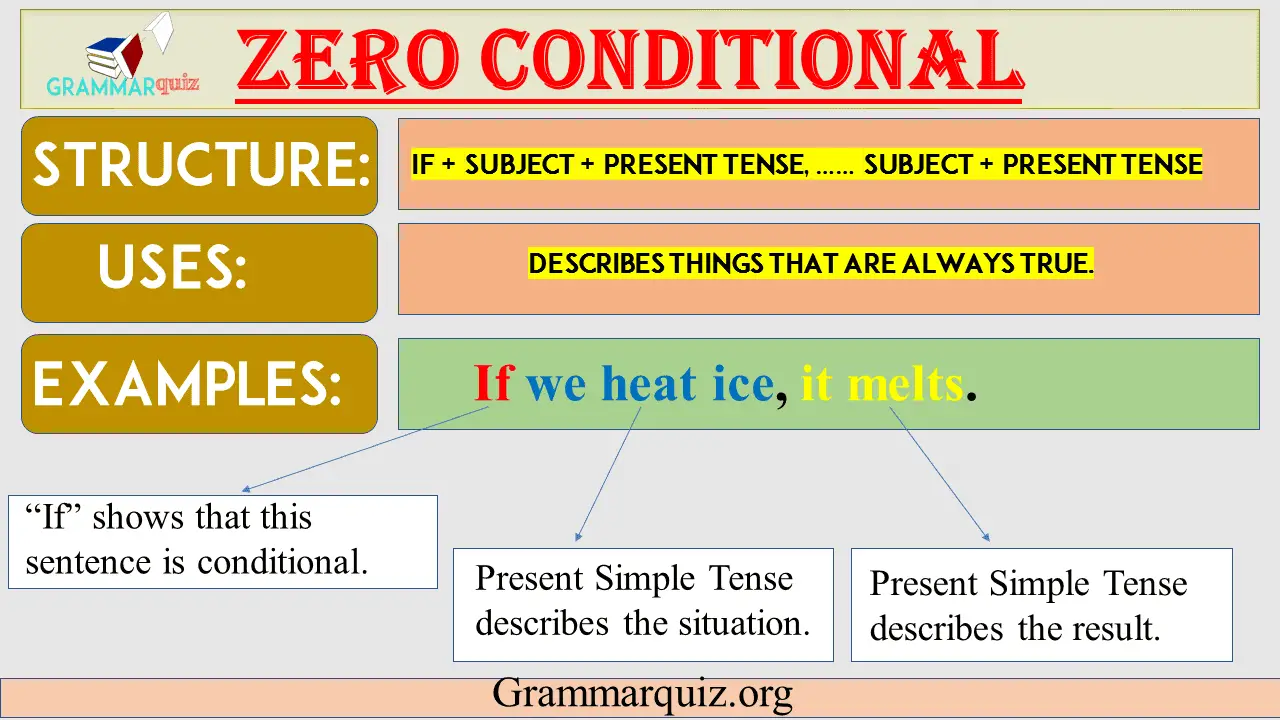
The zero conditional is formed using the present simple tense both in the if and the main clause.
If + Subject + Present Tense, Subject + Present Tense.
We can also invert this structure by placing the main clause first. In this case, we don’t put a comma between the two clauses.
Subject + Present simple If + Subject Present Simple.
We can replace ‘if’ with ‘when’ in a situation where we are sure the action happens.
Must Learn: First Conditional Formula and Uses
Zero Conditional Sentences Examples
- If we boil water, it becomes steam. (Universal truth)
- If we drop something, it falls. (Always true: Anything comes back down every time we drop it.)
- If she gets up early, she always walks. (This statement is generally true: She walks every time she gets up early.)
- If you are learning conditional sentences, you will find this article helpful.
- If it’s cold, I wear a jacket.
- When we put a stone in water, it sinks.
- This thing floats when you put it in water.
- If she loves him, then tell him.
- If they arrive late to the class, the teacher doesn’t let them sit in the class.
- If the boy squawks, everyone in the street hears him.
- When I cut an onion, it makes me cry.
- Plants die If you don’t water them.
- Look for him on the second floor if you reach there late.
- Does the dog bark when you throw a stone on it?
- When the baby is happy, she smiles.
- Chlorine kills bacteria if we put it in water.
- This paper makes a lot of some if we burn it.
- That building looks green when the sunshine on it.
- If we add three and three, we get six.
Zero Conditional Negative Sentences
The zero conditional Sentences is made negative by inserting don’t/does, not after the subject.
- It doesn’t rain if the weather doesn’t get cold.
- Don’t drive a bike if you are under 18.
- He gets angry if his son doesn’t come early at night.
- Don’t talk on your phone If you drive a car.
- If we don’t keep children away from the fire, they burn themselves.
- If you don’t understand these works, look for them in your dictionary.
- Unless the temperature falls below 0o C, the water turns into ice.
- We don’t get warm if the sun doesn’t shine.
- The manager does not let us go home early if we don’t work hard for some hours.
- Unless it rains, the ground doesn’t get wet.
- This glass doesn’t break if you drop it.
- Plants don’t grow well if they don’t get enough water.
- I don’t walk much if it rains every day.
Conditional with Imperatives
An imperative sentence can be used in the result clause of a conditional sentence. A hypothetical situation describes in the if-clause, and the imperative in the main clause describes the suggested action that someone should take if that hypothetical situation happens.
Examples
- If you’re cold, put on a blanket.
- If you feel sick, go to the hospital.
- If they don’t work correctly, call me.
- If she doesn’t respond, ignore her.
- Go to bed early if you are tired.
- Call me if you need more money.
Conditional Related Articles:
- Zero Conditional Examples: 30 Sentences Using Zero Conditional
- 10 Examples of Second Conditional
- 38 Examples of Conditional Sentences
- Mixed Conditional Sentences Formation and Examples
- Third Conditional Sentences- Structure, Uses with Examples
- Second Conditional Sentences: Structure & Examples
- Conditional Sentences Definition, Types and Useful Rules